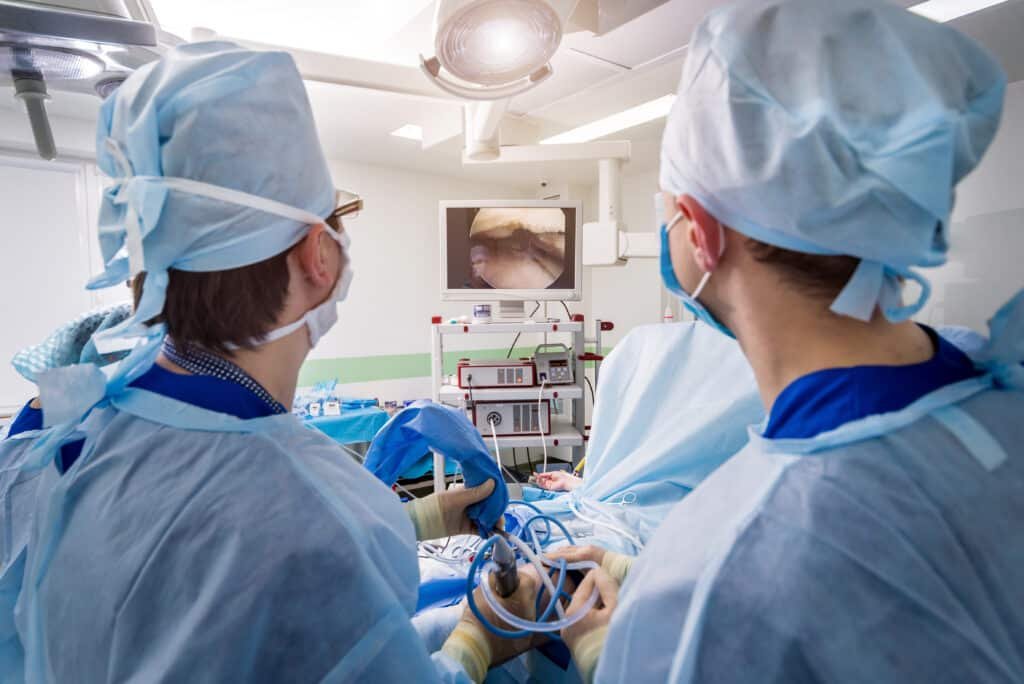
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy stands at the forefront of modern Othopaedic surgery, revolutionizing the way joint disorders and injuries are diagnosed and treated. This minimally invasive procedure offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery, providing patients with faster recovery times, reduced postoperative pain, and smaller incisions.
Understanding Arthroscopy:
Arthroscopy involves the use of a specialized instrument called an arthroscope, which is a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera and light source. This device is inserted into the joint through small incisions, allowing the surgeon to see inside the joint in real-time on a monitor. Additionally, small surgical instruments can be inserted through other incisions to perform necessary repairs or procedures
Applications of Arthroscopy
Knee Arthroscopy
One of the most common uses of arthroscopy is for knee injuries such as torn ligaments (ACL, PCL), meniscal tears, cartilage damage, and synovitis. Surgeons can repair or remove damaged tissue, improving stability and function of the knee joint.
Shoulder Arthroscopy
Arthroscopic procedures are frequently employed to address conditions like rotator cuff tears, shoulder instability, labral tears, and impingement syndrome. This technique allows for precise repair and reconstruction of damaged structures in the shoulder joint.
Hip Arthroscopy
Hip arthroscopy is utilized for various hip conditions including femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), labral tears, hip dysplasia, and synovitis. Surgeons can address these issues through small incisions, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Ankle and Wrist Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy can also be used to diagnose and treat problems in smaller joints like the ankle and wrist. Common issues include ligament tears, cartilage injuries, and joint instability, which can be effectively managed through arthroscopic techniques.
Benefits of Arthroscopy:
- Minimally Invasive : Arthroscopy requires only small incisions, resulting in less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and faster recovery times compared to open surgery.
- Accurate Diagnosis : The high-definition camera of the arthroscope allows for detailed visualization of the joint, aiding in accurate diagnosis of the underlying problem.
- Targeted Treatment : Surgeons can precisely target and address the specific issue within the joint, leading to better outcomes and decreased risk of complications.
- Outpatient Procedure : Many arthroscopic surgeries can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day and resume normal activities sooner.




