Uni Condylar Knee Replacement
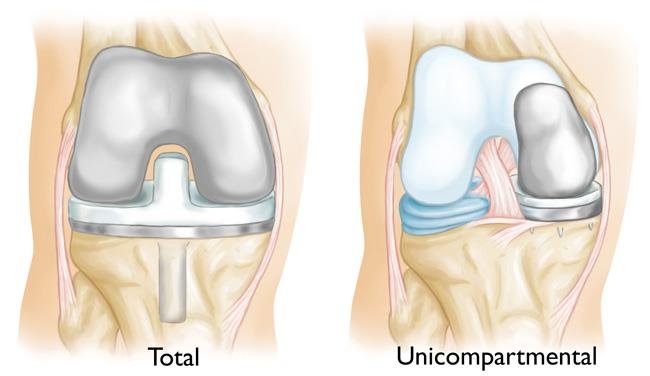
Uni Condylar Knee Replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement or partial knee replacement, is a surgical procedure used to treat osteoarthritis in one compartment of the knee. Unlike total knee replacement, which involves replacing all three compartments of the knee joint, uni condylar knee replacement focuses on replacing only the damaged portion of the knee joint.
The knee joint is composed of three compartments: the medial compartment (inside part of the knee), the lateral compartment (outside part of the knee), and the patellofemoral compartment (the area behind the kneecap). Osteoarthritis can affect one or more of these compartments, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility.
Uni condylar knee replacement is typically recommended for patients with osteoarthritis confined to one compartment of the knee, where the damage is limited and the surrounding ligaments and cartilage are relatively intact. It is not suitable for individuals with widespread arthritis affecting multiple compartments or those with significant ligament instability.
Benefits of uni condylar knee replacement include:
- Preservation of healthy bone and tissue: Since only the damaged portion of the knee joint is replaced, healthy bone and tissue in the unaffected compartments are preserved.
- Faster recovery: Uni condylar knee replacement typically involves a smaller incision and less trauma to surrounding tissues compared to total knee replacement, leading to a faster recovery and shorter hospital stay.
- Improved range of motion: Patients often experience improved range of motion and flexibility in the affected knee following uni condylar knee replacement surgery.
- Reduced pain: By replacing the damaged portion of the knee joint, uni condylar knee replacement can significantly reduce pain and discomfort associated with osteoarthritis.
- Less invasive: Uni condylar knee replacement is a less invasive procedure compared to total knee replacement, making it a suitable option for patients who may not be candidates for more extensive surgery.




